Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) have emerged as a pivotal investment vehicle, allowing both individual and institutional investors to gain exposure to the real estate market without the complexities of direct property ownership. This guide delves into the intricacies of REITs, offering comprehensive insights into how they work, their types, benefits, limitations, and strategies for successful investment.
What Are Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)?
A Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) is a corporation that owns, operates, or finances income-generating real estate. By pooling the capital of numerous investors, REITs allow individuals to earn dividends from real estate investments without having to buy, manage, or finance any properties themselves. REITs typically manage portfolios of high-value properties, which can include office buildings, shopping malls, apartments, hotels, resorts, and even infrastructure like data centers and healthcare facilities.
How REITs Generate Income
REITs primarily generate income through leasing space and collecting rents on the properties they own. This income is then distributed among shareholders as dividends. Additionally, some REITs generate income by financing real estate and earning interest on mortgages or other real estate loans.
Types of Real Estate Investment Trusts
REITs are broadly categorized based on the nature of their business and the way they are traded. Understanding these types is crucial for investors to align their investment strategy with their financial goals.
1. Equity REITs
Equity REITs are the most common type and focus on owning and operating income-generating properties. The primary source of revenue for these REITs is rental income, making them an attractive option for investors seeking steady dividend income.
2. Mortgage REITs (mREITs)
Mortgage REITs, or mREITs, differ from equity REITs in that they invest in real estate debt rather than equity. These REITs lend money directly to real estate owners or acquire mortgage-backed securities. Income for mREITs is generated from the interest on these loans.
3. Hybrid REITs
Hybrid REITs offer a combination of both equity and mortgage REIT characteristics. They invest in both properties and real estate loans, providing diversified income streams from both rents and interest.
4. Publicly Traded REITs
Publicly traded REITs are listed on major stock exchanges, allowing investors to buy and sell shares easily. These REITs are regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), ensuring transparency and investor protection.
5. Public Non-Traded REITs
Public non-traded REITs are registered with SEBI but are not listed on any stock exchanges. While they offer potential for high yields and are less susceptible to market fluctuations, they are less liquid compared to publicly traded REITs.
6. Private REITs
Private REITs are not traded on public exchanges and are typically available only to accredited investors. They offer limited liquidity and are not subject to the same regulatory scrutiny as public REITs.
Benefits of Investing in REITs
Investing in REITs offers several advantages, making them an appealing option for both novice and experienced investors.
1. Steady Dividend Income
REITs are required to distribute at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders in the form of dividends. This requirement ensures that investors receive a consistent stream of income.
2. Portfolio Diversification
REITs provide an opportunity to diversify an investment portfolio. By investing in REITs, investors can gain exposure to the real estate market, which behaves differently than stocks and bonds.
3. Liquidity
Most REITs are publicly traded, allowing investors to buy and sell shares with ease. This liquidity is a significant advantage compared to direct real estate investments, which can be time-consuming and costly to sell.
4. Transparency and Regulation
REITs are subject to stringent regulatory requirements, including regular financial disclosures and audits. This transparency helps investors make informed decisions and ensures a higher level of trust.
5. Inflation Hedge
Real estate has historically been an effective hedge against inflation. As property values and rents increase with inflation, so does the income generated by REITs, protecting investors’ purchasing power.
Limitations of REITs
While REITs offer numerous benefits, there are also some limitations that investors should be aware of.
1. Taxation
Dividends paid by REITs are typically taxed as ordinary income, which can be a disadvantage for investors in higher tax brackets.
2. Market Risk
Publicly traded REITs are subject to market fluctuations, which can impact the value of shares. Economic downturns and changes in interest rates can also affect the performance of REITs.
3. High Management Fees
Some REITs, particularly private and non-traded REITs, may charge high management and transaction fees, which can eat into investors’ returns.
4. Limited Growth Potential
Because REITs are required to distribute most of their income, they have limited funds available for reinvestment. This can restrict their ability to grow and increase the value of their properties over time.
How to Invest in REITs
Investing in REITs is straightforward and can be done through various channels depending on your investment goals and preferences.
1. Direct Purchase of REIT Shares
Investors can buy shares of publicly traded REITs through a brokerage account, just like they would with any other stock. This method offers liquidity and the ability to diversify within the real estate sector.
2. Mutual Funds and ETFs
REIT mutual funds and ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) offer a way to invest in a diversified portfolio of REITs. These funds are managed by professionals and provide exposure to a broad range of real estate investments.
3. Private REITs
For accredited investors, private REITs offer the opportunity to invest in real estate with potentially higher returns but less liquidity. These REITs are often not available to the general public and require a larger initial investment.
Role of REITs in a Retirement Portfolio
Including REITs in a retirement portfolio can be a smart strategy for investors looking to generate steady income and achieve long-term growth.
1. Diversification
REITs add a layer of diversification to retirement portfolios, reducing the overall risk by spreading investments across different asset classes.
2. Long-Term Growth
REITs are more closely aligned with the long-term cycles of the real estate market, making them suitable for investors with a long investment horizon.
3. Income Generation
The consistent dividend payments from REITs can provide a reliable source of income in retirement, helping to supplement other income sources like pensions and social security.
Tips for Assessing REIT Investments
When evaluating REITs, investors should consider several key factors to ensure they are making informed decisions.
1. Dividend Yield
Look for REITs with a strong history of paying dividends. The dividend yield is a crucial indicator of the income potential of the investment.
2. Property Diversification
REITs that own a diverse range of properties and have a broad tenant base are generally less risky and more resilient to economic downturns.
3. Management Team
A REIT’s management team plays a critical role in its success. Investors should look for REITs with experienced and reputable management teams.
4. Fund From Operations (FFO)
Fund From Operations (FFO) is a key metric used to evaluate a REIT’s performance. It provides a clearer picture of the REIT’s cash flow and is a better indicator of financial health than net income.
5. Growth Prospects
Consider the REIT’s strategy for growth, including its pipeline of property acquisitions and development projects. A REIT with strong growth prospects is more likely to deliver higher returns over time.
REIT Structure
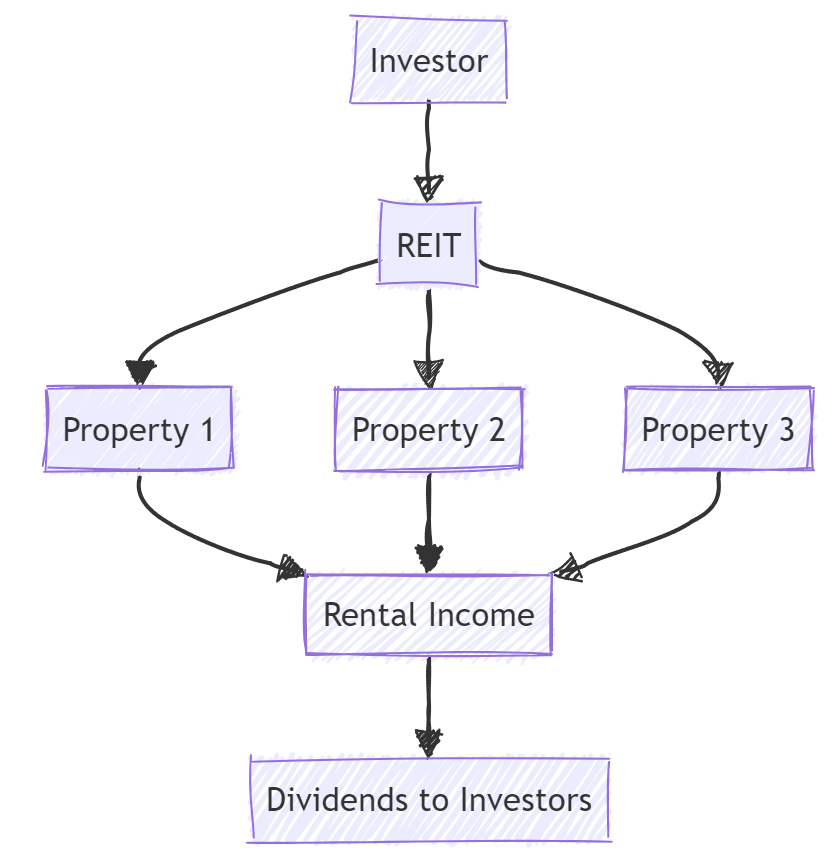
This diagram illustrates the basic structure of a REIT, showing how investors contribute capital, which is then used by the REIT to purchase and manage properties, ultimately generating rental income that is distributed back to investors as dividends.
Also Read: Is Fractional Ownership of Real Estate Safe? Exploring Investment Options, Notable Platforms, and SEBI’s Role in Enhancing Security
REITs offer a unique and accessible way for investors to participate in the real estate market, providing opportunities for income generation, portfolio diversification, and long-term growth. By understanding the different types of REITs, their benefits and limitations, and the strategies for effective investment, investors can make informed decisions and enhance their financial portfolios. Whether you’re looking to diversify your retirement portfolio or seeking a steady income stream, REITs can be a valuable addition to your investment strategy.
Subscribe to get updates on our latest posts and market trends.






Join The Discussion